When I mention diseases such as arthritis, arthrosis, joint problems inevitably come to mind. In fact, both of these pathologies are directly related to the musculoskeletal system, since the pathological process is localized in the articular joints. Both arthritis and arthrosis have similar symptoms. Many patients confuse these diseases and consider them as one and the same pathology, however, they have essential differences.
What is arthritis and arthrosis and how do they differ?
Arthritis and arthrosis are common diagnoses in elderly patients. To understand the differences between these two pathologies, let's consider what arthritis and arthrosis are and what is the difference between them.
A chronic disease of the joints, in which their gradual deformation is observed, is called arthrosis. A more accurate name is osteoarthritis, since the pathological process involves not only cartilage, but ultimately bone tissue as well.
The immediate cause of the disease is damage to the joint surfaces, as a result of which they wear out and cease to perform their functions. A typical manifestation of arthrosis is severe pain during limb movement; as a result of the worsening of the pathological process, the mobility of the joint is significantly limited. In an advanced stage, the joint may become immobile.
Osteoarthritis usually occurs in people over forty-five years of age, but in rare cases it can affect the joints of young people. The disease develops mainly in women and also affects people with congenital pathologies of the limbs. Osteoarthritis is caused by excess weight, joint surgery and injuries, for example, to the hip or knee joint. Endogenous factors, such as poor nutrition or blood circulation disorders in the joints, can also cause the disease.
Arthritis is an inflammatory pathology localized in the joints. This is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis. Inflammation can appear as a result of joint infection, damage, as well as due to degenerative changes in the tissue. Like osteoarthritis, arthritis is characterized by joint pain that worsens with movement.
Lack of proper treatment leads to loss of mobility of the joint and its complete immobilization. Arthritis is more easily recognized, as inflammation provokes redness of the skin at the site of the lesion and swelling. Note that arthritis is not an isolated pathology. This is a systemic disease that affects not only the musculoskeletal system. Arthritis usually affects the liver, kidneys and heart. This is the main difference between arthritis and local arthrosis.
signs
The symptoms of arthritis and arthrosis are mostly similar, but they also have important differences. Pain is a core symptom that comes to the fore in both arthrosis and arthritis. The nature of the pain varies: with arthrosis, patients experience negative sensations during physical activity, as well as when the load on the damaged joint increases.
In the initial stage, the pain may not be strong. Because of this, patients do not always pay attention to such symptoms and do not pay attention to the first signs of pathology. At rest, the pain subsides. Only in the second and third stages is the pain constantly present. However, if you position the limb well, the pain will decrease. With arthritis, the pain does not decrease, and the highest peak of its development is reached at night, closer to the morning.
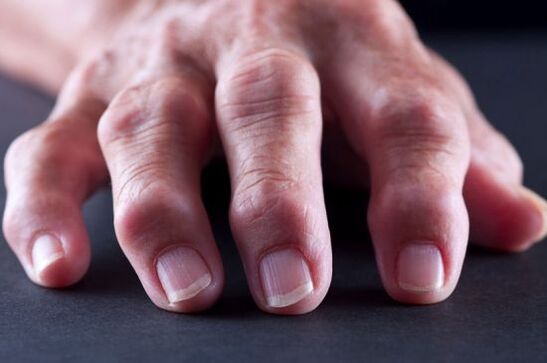
Crackling is a typical characteristic of arthrosis and chronic arthritis.
A crack occurs due to a decrease in the elasticity of cartilage tissue and an increase in friction between the articular surfaces. In the initial stage, you may notice a tingling of the fingers, and then the larger joints are affected. A distinctive feature of joint cracking is the harsh, dry sound produced by the joint.
Limitation of joint mobility and stiffness in movement are typical symptoms of arthrosis and arthritis, but for arthrosis joint problems differ in location, d. m. th. a specific joint is affected, and with arthritis - a systemic pathology - discomfort is observed not only in the joint, but in the whole body.
In both pathologies, joint deformities are observed, but they have distinctive features. With arthrosis, the changes affect only the joint itself, and the inflammatory process in arthritis provokes changes in the skin - you can see swelling, redness and hyperthermia. In addition, arthritis is accompanied by general somatic pathology: the body temperature rises, a typical state of fever appears, sweating increases, weakness and drowsiness appear. Conjunctivitis may begin and chronic diseases may become more complicated. With arthrosis there are no such symptoms, but if arthrosis has developed, then inflammation will also accompany arthrosis.
The doctor must carefully differentiate the signs of arthritis and arthrosis, so if negative symptoms appear, consultation with a specialist is required.
Diagnosing
To start treating the disease, the correct diagnosis of arthritis or arthrosis is important. This can be done using various research techniques. Not all patients know which doctor deals with joint pathologies, so at the initial stage you can contact a rheumatologist or therapist, and then you will need to consult an orthopedist or surgeon.
Patients are asked to undergo a blood test, which will demonstrate general changes in the body. If the results of a blood test do not show any abnormalities, then doctors are inclined towards arthrosis as a preliminary diagnosis.
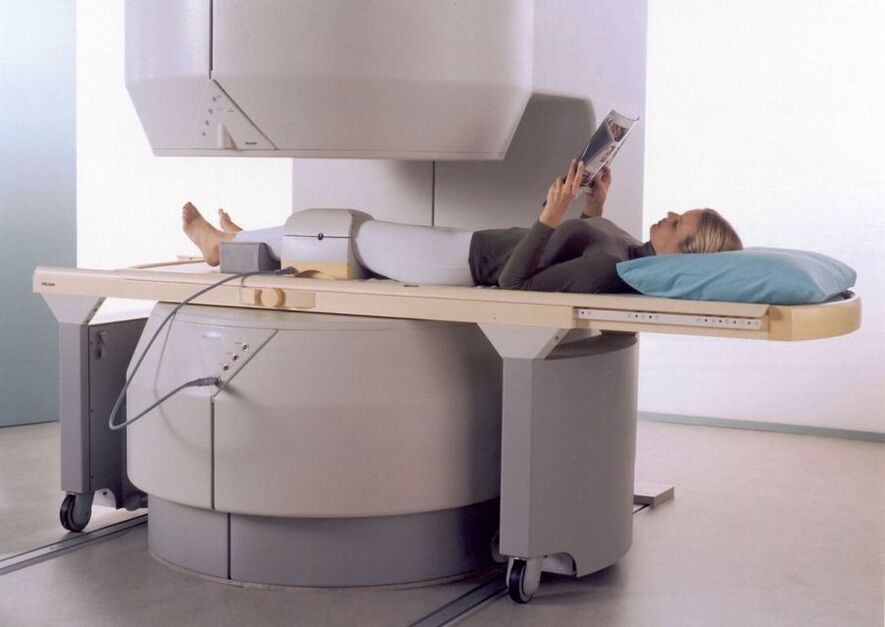
If the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes in the blood plasma increases, rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, as there is a clear indication of an inflammatory process. Usually the speed increases above 25 mm/h. Another confirmatory sign will be joint pain that worsens at night. To be fair, we note that an increase in ESR is possible even with arthrosis, if it is accompanied by inflammation.
An additional argument in favor of rheumatoid arthritis will be the increase in the number of leukocytes. Blood is also taken from a vein for rheumatological analysis - the appearance of a special marker - C-reactive protein, which indicates inflammation. However, you should not rely only on a blood test, as it is impossible to reliably determine one of the diseases using this analysis. It is necessary to carry out additional research, constantly taking into account the presence of an inflammatory factor in the blood.
As additional tests, doctors prescribe the following to the patient:
- X-ray of the problem area;
- magnetic resonance;
- computed tomography;
- radioisotope scanning.
Doctors take into account the tests, a carefully collected medical history and the results of a blood test, after which a particular disease is diagnosed.
Treatment
For the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis to be successful, it is necessary to choose the right treatment strategy. Note that it is not always possible to completely cure the disease, and in some cases long-term remission is considered a great success.
To alleviate the deterioration and prevent the return of diseases, it is necessary to treat with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines have a particularly powerful effect on the body with arthritis, and also affect the positive dynamics of arthrosis.
Features of the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are as follows:
- It is not recommended to take drugs for a long time, even if they do not cause negative effects during administration;
- patients with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidney and heart disorders are prohibited from taking NSAIDs;
- Do not increase the dose of drugs without the doctor's permission, as a negative reaction may occur if individual sensitivity occurs;
- When taking medications, you should take them with a large glass of water;
- when taking NSAIDs, it is forbidden to combine some drugs, as well as drink alcoholic beverages;
- Taking NSAIDs during pregnancy is prohibited.
When you contact a doctor, the patient will be prescribed effective treatment with the safest non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after the examination. Basically, all drugs of this group can be divided into inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 1 and 2. COX-2 inhibitors are considered to be more loyal to the body's drugs.
First and second generation inhibitors are included in many drugs. These are ointments, patches, gels and tablet preparations.
Medicines to relieve muscle spasms - muscle relaxants - will be helpful in treatment. Typically, this often happens in patients suffering from arthrosis or arthritis. With severe pain in the joints, the muscles experience strong tension and with prolonged discomfort suffer from a lack of food and oxygen, so it is very important to immediately relieve the discomfort that accompanies the disease.
During therapy, a necessary condition is the normalization of metabolic processes. This becomes possible as inflammation decreases and muscle spasm is relieved. Metabolic drugs for patients with arthritis and arthrosis are adenosine triphosphoric acid, inosine, adenosine phosphate, B vitamins, anabolic steroids.
To remove salts from arthrosis, a special series of medications are prescribed, as well as tools to achieve an optimal acid-base balance.
To cure arthritis and arthrosis or to achieve a stable positive dynamic, it is very important to take all the medications recommended by your doctor. Moreover, this should be done according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, because even the most effective metabolic agents against the background of an active inflammatory process will simply be useless.
Traditional treatment
Diseases such as arthritis and arthrosis can be treated not only with traditional medicines, but also with folk remedies. Massages with preparations based on natural ingredients will be useful. These are bee and snake venom ointments. These preparations also include essential oils. During the massage, you can add eucalyptus oil and ginger, ginger, basil, rosemary or juniper oil.
For arthritis and arthrosis, warm baths have a good relaxing effect. They will help relieve muscle pain and fatigue and help relax the body as a whole. The best combination is one drop of ginger oil and the same amount of styrax benzoin or two drops of basil oil and black pepper to one tablespoon of olive oil. Add 15-20 drops to the bath. The recipe helps well if the patient has arthrosis of the feet. Oil baths can be done every evening at night.
Black poplar also has an excellent effect. Not all patients know how to treat arthritis and arthrosis with black poplar, but it is very simple to do. From a healthy tree, you need to collect rot, young leaves and shoots - about half a bucket, after which it is all poured with boiling water to the edge of the container and kept overnight. In the morning, the juice is carefully poured into the bath, leaving the dessert, and soaked in it for half an hour. After a shower, it is advisable to warm up and lie down in bed for an hour.
Folk remedies help a lot even if the patient is affected by arthrosis - a severe combination of bone deformations together with the inflammatory process in the articular joint. To treat it, you need to take a glass of fir needles and fill them with two liters of water. It is necessary to boil the product for fifteen minutes, after which the soup is poured into the bath and taken until the water cools completely.
Senna leaves will help with arthritis and arthrosis. If the patient regularly treats the disease with this medicine, the inflammation goes away quickly. Senna is used as follows: two glasses of the dry ingredient are poured with a liter of boiling water and closed for forty minutes. The liquid is then poured into the bath, sea salt is added there and it is taken until the water is at the optimal temperature. After the bath, areas of damage due to arthrosis or arthritis are treated with fir oil and wrapped with a scarf.
Preventing
As a preventive measure, doctors give the following advice to patients:
- fully treat all infectious pathologies, do not interrupt the course of therapy with antibacterial drugs, so as not to leave pockets of inflammation in the body;
- follow a balanced diet;
- wear comfortable shoes that do not restrict your feet;
- get rid of excess weight, which creates additional stress on the limb;
- don't get your feet too cold, take care in wet weather and cold seasons;
- protect yourself from injuries and when actively playing sports, use bandages, supports and special elastic bandages;
- perform daily gymnastics, take walks in the fresh air to activate blood circulation in the body, and when the first symptoms of arthritis or arthrosis are detected, do special joint gymnastics - exercises for hands, wrists, knees.
Arthritis and arthrosis are serious lesions of the articular surfaces. If treated incorrectly or in time, they can lead to disability, so doctors strongly recommend that you consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.



















